Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable agricultural system that combines fish farming and hydroponic gardening. By utilizing the waste produced by fish as a nutrient-rich fertilizer for plants, aquaponics offers a symbiotic relationship between aquatic animals and plants. This unique method of cultivation has gained popularity in recent years due to its efficiency, environmental benefits, and potential for year-round production. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of aquaponics, its benefits, the role of fish and plants, and how to get started with your aquaponics garden.
Introduction to Aquaponics: What is it, and how does it work?
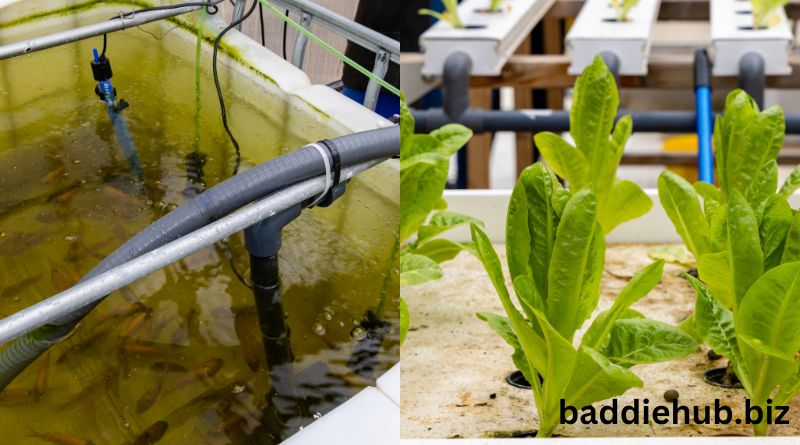
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) in a symbiotic manner. The concept is simple yet effective: fish produce waste in the form of ammonia-rich water, which is harmful to them if not removed. In traditional aquaculture systems, this waste is often disposed of, leading to water pollution. However, in an aquaponics system, this waste is a valuable resource.
The wastewater from the fish tank is pumped into the hydroponic grow beds, where bacteria break down the ammonia into nitrates, which the plants then absorb as nutrients. This process cleans the water for the fish, creating a natural and sustainable environment for both aquatic animals and plants. The plants, in turn, filter the water and return it to the fish tank, completing the cycle.
Benefits of Aquaponics: Sustainability, efficiency, and environmental impact
Aquaponics offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive alternative to traditional agricultural methods. Firstly, it is an incredibly sustainable system. By reusing water and minimizing waste, aquaponics conserves resources and reduces water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional soil-based farming. It also eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Furthermore, aquaponics is highly efficient. The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants allows for faster growth rates and higher yields. In fact, plants in an aquaponics system can grow up to twice as fast as those in traditional soil-based gardens. Additionally, because the system is closed-loop, it can be operated in any location, regardless of soil quality or climate conditions. This makes aquaponics a viable option for urban areas or regions with limited arable land.
Fish Farming: Understanding the role of fish in the aquaponics system
Fish play a crucial role in an aquaponics system. They provide the necessary nutrients for plant growth through their waste. However, not all fish are suitable for aquaponics. The ideal fish species for aquaponics are those that can tolerate fluctuating water conditions and produce ample waste. Tilapia, trout, and catfish are commonly used in commercial aquaponics systems due to their hardiness and fast growth rates.
Fish require proper feeding and care to ensure their health and productivity. In an aquaponics system, they are fed a balanced diet, and their waste is continuously monitored. The ammonia levels in the water must be kept within a safe range to prevent harm to the fish and maintain water quality. Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the well-being of the fish and the success of the aquaponics system.
Hydroponic Gardening: The basics of growing plants without soil
Hydroponic gardening, the other half of aquaponics, involves growing plants without soil. Instead of relying on soil for nutrients, plants in a hydroponic system receive all necessary nutrients through a nutrient-rich water solution. This method allows for precise control over the plant’s growing conditions, including pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and water availability.
Several hydroponic techniques can be used in aquaponics, including nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and media-based systems. NFT involves a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over the plant roots, while DWC suspends the plant roots directly in the nutrient solution. Media-based systems use materials like perlite or coconut coir to support the plants and provide aeration to the roots.
In aquaponics, the hydroponic grow beds act as filters for the fish waste. The plants absorb the nutrients from the water, effectively removing harmful substances and purifying them for the fish. This interdependence between fish and plants creates a sustainable and balanced ecosystem.
Merging Fish Farming and Hydroponic Gardening: How the two systems work together
The integration of fish farming and hydroponic gardening in aquaponics is what sets it apart from other agricultural methods. The waste produced by the fish acts as a natural fertilizer for the plants, providing them with essential nutrients. As the plants absorb these nutrients, they filter the water, removing toxins and creating a healthy environment for the fish.
The fish and plants in an aquaponics system rely on each other for survival. The fish provide the plants with nutrients, while the plants purify the water for the fish. This mutualistic relationship creates a sustainable and self-regulating system that requires minimal intervention.
The integration of these two systems also allows for year-round production. Aquaponics can be operated indoors, utilizing artificial lighting and climate control to create optimal growing conditions. This means that fresh produce can be grown consistently, regardless of the season or external climate. Furthermore, the absence of soil eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, reducing the need for pesticides and herbicides.
Choosing the Right Plants for Aquaponics: Factors to consider and recommended plant species
When selecting plants for an aquaponics system, several factors need to be considered. These include the plant’s nutrient requirements, growth habits, and compatibility with the specific conditions of the system. Leafy greens, such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, are popular choices for aquaponics due to their high nutrient content and fast growth rates.
Herbs like basil, mint, and parsley also thrive in aquaponics systems and add flavor to dishes. Fruit-bearing plants, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers, can also be grown successfully in aquaponics, although they may require additional support for their growth.
It is essential to choose plant species that are well-suited to the specific climate and environmental conditions of the aquaponics system. Some plants may require warmer temperatures, while others may be more tolerant of cooler climates. Researching and selecting the right plant species will ensure optimal growth and productivity in your aquaponics garden.
Climate Considerations: Adapting aquaponics to different climates and regions
One of the advantages of aquaponics is its adaptability to different climates and regions. The closed-loop system allows for precise control over environmental conditions, making it possible to grow plants in areas with unfavorable climates or limited arable land.
In colder climates, additional heating may be required to maintain the optimal temperature for both fish and plants. This can be achieved through various methods, such as using insulated greenhouses, heaters, or geothermal energy. On the other hand, in hot climates, cooling systems or shade structures may be necessary to prevent water and plants from overheating.
It is also important to consider the availability of natural light in the location of the aquaponics system. While artificial lighting can be used to supplement or replace natural light, the intensity and duration of light exposure should be carefully monitored to ensure optimal plant growth.
Aquaponics and Pot Seeds
As the legalization and acceptance of weed continue to grow, many growers are exploring alternative cultivation methods, including aquaponics. Growing weed in aquaponics systems offers several advantages over traditional soil-based methods. The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants provides a nutrient-rich environment for marijuana plants, resulting in faster growth and higher yields.
Aquaponics eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, making it a natural and organic method of growing marijuana. The absence of soil also reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, minimizing the need for chemical interventions.
When growing growers choice seeds weed seeds in aquaponics, it is important to select the right strains that are suitable for the specific conditions of the system. Some strains may require more nutrients or have specific light cycle requirements. Additionally, proper care and monitoring of the fish and water quality are essential to ensure the health and productivity of the marijuana plants.
Getting Started with Aquaponics: Tips for setting up your own aquaponics garden
Setting up an aquaponics garden can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, here are some tips to help you get started:
- Research and educate yourself: Familiarize yourself with the principles and techniques of aquaponics. Understand the requirements of fish and plants, as well as the necessary equipment and maintenance.
- Start small: Begin with a small-scale system to gain hands-on experience and learn from any mistakes. As you become more confident, you can gradually expand your garden.
- Choose the right fish: Select fish species that are suitable for your climate and system size. Consider factors such as water temperature, oxygen requirements, and compatibility with the plants you wish to grow.
- Balance the system: Maintain a proper balance between fish and plants. Avoid overstocking the fish tank and ensure that the plants have enough nutrients to thrive.
- Monitor water quality: Regularly test the water parameters, including pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. Make adjustments as necessary to maintain optimal conditions for both fish and plants.
- Be patient and observant: Aquaponics is a dynamic system that requires time and attention. Observe the behavior of your fish and the growth of your plants to detect any issues early on.
Aquaponics vs. Traditional Agriculture: A comparison of the two methods
Aquaponics and traditional agriculture are two fundamentally different approaches to cultivation. While both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, aquaponics offers several distinct benefits over traditional agriculture:
- Water conservation: Aquaponics uses significantly less water compared to traditional agriculture, as water is recycled within the closed-loop system.
- Nutrient recycling: In aquaponics, nutrients are continuously recycled and reused, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Year-round production: Aquaponics can be operated indoors, allowing for year-round production regardless of external climate conditions. Traditional agriculture is often limited to specific growing seasons.
- Space efficiency: Aquaponics can be implemented in small spaces, making it suitable for urban areas or regions with limited arable land.
- Environmental impact: Aquaponics eliminates the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, reducing the environmental impact and promoting natural and organic cultivation.
However, traditional agriculture also has its merits, such as a wider variety of crop options and the ability to incorporate traditional farming practices. Both methods have their place in the agricultural landscape, and the choice ultimately depends on the specific needs and goals of the grower.
Conclusion: The future of aquaponics and its potential impact on agriculture
Aquaponics represents a promising and sustainable approach to agriculture that combines the best of fish farming and hydroponic gardening. Its ability to conserve water, utilize waste, and produce high yields makes it an attractive alternative to traditional farming methods. With advancements in technology and increased awareness of the environmental impact of conventional agriculture, aquaponics is poised to play a significant role in the future of food production.
As more people embrace the benefits of aquaponics, it is likely to become more accessible and widespread. Its adaptability to various climates and the potential for year-round production make it an ideal solution for addressing food scarcity and promoting self-sufficiency. By merging the principles of fish farming and hydroponic gardening, aquaponics offers a sustainable and efficient method of cultivation with the potential to revolutionize the way we grow food.